Sorensen Clinic
Plastic and Reconstructive Surgery
10 Knaresborough Place
Kensington
London SW5 0TG
United Kingdom
Appointments: +44 (0) 20 7600 4444
Email: info@sorensenclinic.com
Office hours
Monday - Friday: 09.00 - 17.30
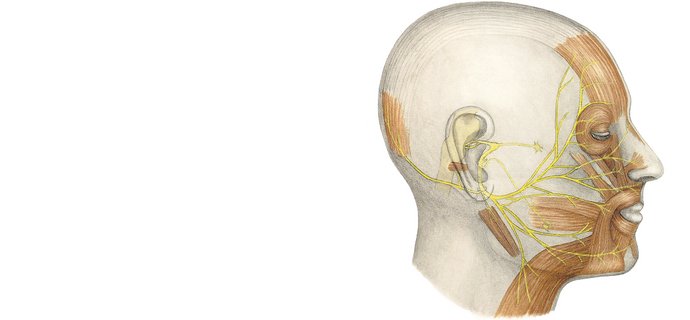
The branches and sub branches of the Trigeminal nerve enter the soft tissues of the face through small holes in the cranium. If a major neural pathway is disrupted (divided, blocked or compressed) by fractures of facial bone or soft tissue lacerations, microsurgical intervention may be necessary in order to recover sensation in the area controlled by the nerve branch.
While loss of sensitivity in some parts of the human body poses a minor problem, loss of sensation in/around the mouth, lips or eyes is distressing and justifies surgery.
Unlike motor nerve injury, the time between injury and repair is less critical for sensory nerves, and sensation in the face can be recovered 1-2 years after injury. Sensory nerves can be accessed by various routes, all of which leave minimal scarring. Peripheral nerves have potential for self-repair, but it is a slow process that may take 3-4 months or longer. Minor and superficial nerve injuries will often heal themselves. Examination, neurophysiology and clinical imaging will determine whether the injured nerve needs repair, and if so, the options for surgical reconstruction.
Candidates are patients with persistent loss of sensation in part of the face after trauma or surgery (more than 4-6 months).