Sorensen Clinic
Plastic and Reconstructive Surgery
10 Knaresborough Place
Kensington
London SW5 0TG
United Kingdom
Appointments: +44 (0) 20 7600 4444
Email: info@sorensenclinic.com
Office hours
Monday - Friday: 09.00 - 17.30
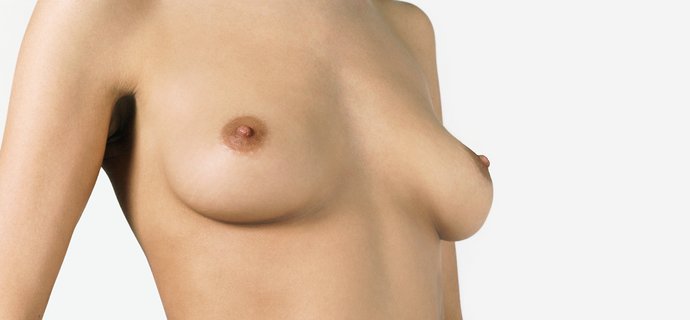
The tubular breast is an uncommon breast condition, known under several names such as tubular breast deformity, tuberous breasts, breast tissue hypoplasia, constricted breasts or ‘snoopy breasts’. The extent of the deformity can range from mild to severe, with typical characteristics including a constricted breast base (occasionally with the breast appearing as a tube), areolar herniation, wide spacing between the breasts and underdeveloped breast tissue (hypoplasia).
The disorder is often noticed after puberty as an ‘odd breast shape’, but as the mildest grade I is also the most frequent, many young women are not aware that they have a treatable deformity until later in life.
The treatment for tubular breasts is unlike any other aesthetic breast surgeries and is strategically aimed at enhancing breast width, symmetry and fullness to include a rounded lower breast curve. It therefore often includes components of breast augmentation surgery, periareolar breast lift and breast asymmetry correction within the same surgical procedure. The choice of operative technique involves careful analysis and discussion during consultation.
Dr Sorensen uses a highly specialised treatment that combines several techniques for breast enhancement and allows for customisation according to body proportions, asymmetries and the breast tissue available.
Although the clinical condition varies considerably; from almost non-existent breast tissue to constricted asymmetries, the treatments used are able to restore both breast base and breast shape. Anatomical breast implants are especially important in achieving an aesthetic breast shape. A range of specialised techniques will help to release constrictions and preserve glandular tissue and milk ducts, allowing for future breastfeeding whenever possible.
A secondary fat grafting procedure may be indicated 3-4 months after surgery to further refine shape and aesthetic outcome.
Any woman with tubular breast deformity will experience a significant aesthetic improvement to her breast shape and overall appearance. It is important that the breasts are not still in the process of development but have matured to their full extent. Most women are in their twenties and thirties when they have their correction, however some women do not recognise that they have a treatable breast condition and have correction performed later in life.
Tubular Breast Classification
Tubular breast deformities are classified according to the breast base and severity of constriction (Grolleau):
● Grade I, light hypoplasia: Breast deficient in the lower inner quadrant.
● Grade II, moderate hypoplasia: Breast deficient in both lower quadrants.
● Grade III, severe hypoplasia: Breast deficient in all four quadrants with constriction of breast base horisontally and vertically.